
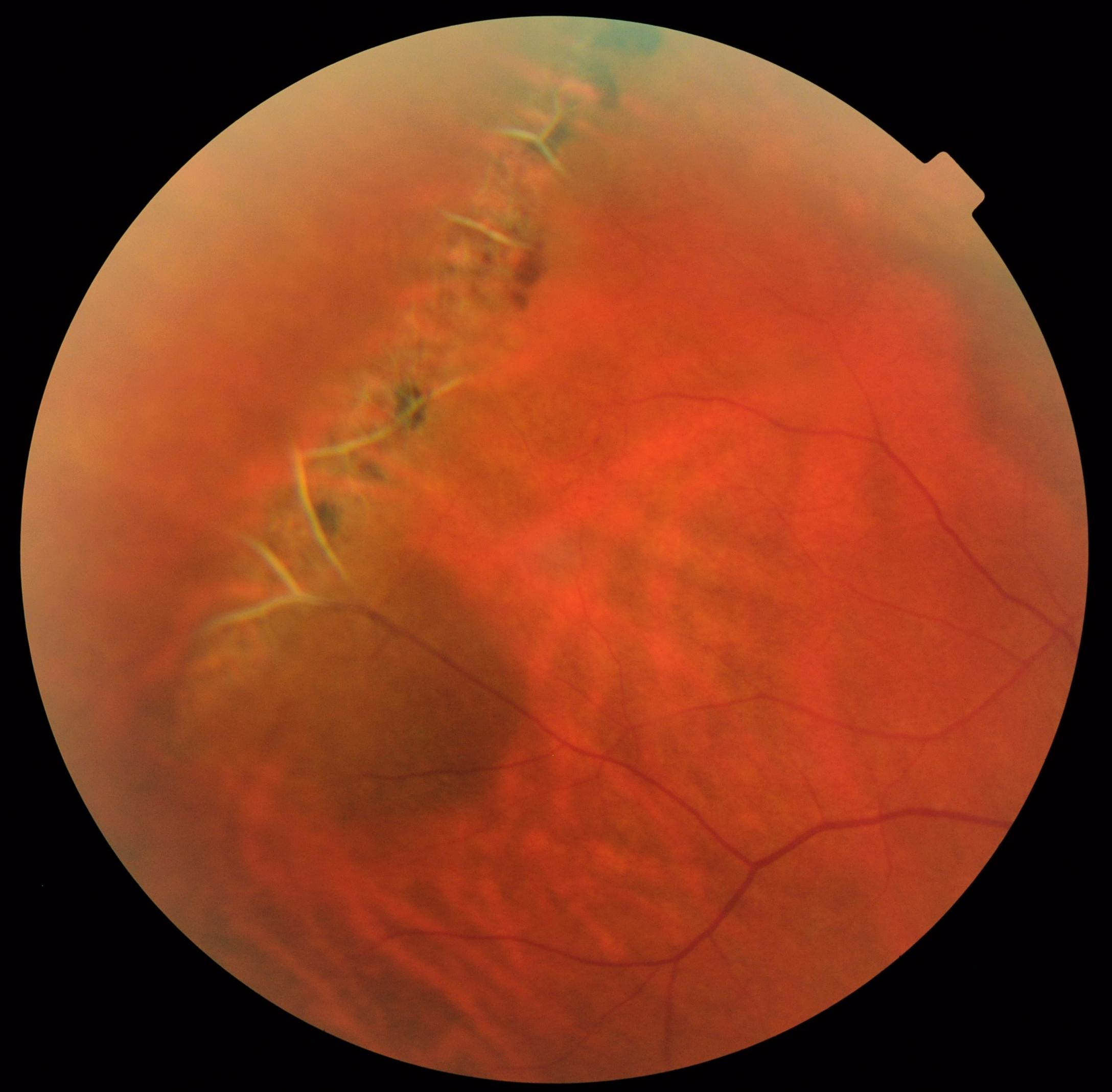
Laser photocoagulation has been shown to reduce risks of retinal detachment in symptomatic lattice degeneration. It is not known if surgical interventions such as laser photocoagulation or cryotherapy is effective in preventing retinal detachment in patients with lattice degeneration or asymptomatic retinal detachment. The most important factors generating a detachment from a retinal break include centripetal vitreoretinal traction at the edge of a retinal break and the flow of liquefied vitreous through a retinal break into the subretinal space. Treatment īarrage laser is at times done prophylactically around a hole or tear associated with lattice degeneration in an eye at risk of developing a retinal detachment. Risk of developing lattice degeneration in one eye is also increased if lattice degeneration is already present in the other eye. It usually shows an autosomal dominant pattern and occurs in. Although the overall risk is low (around 1), lattice degeneration and atrophic. Is Lattice Degeneration common It occurs in 78 of the general. Lattice degeneration is a very common, inherited, congenital abnormality of the peripheral retina. They may be tumorous, vascular, degenerative, inflammatory, traumatic. Theright eye presented myopic degenerative changes. I28) shows the appearance ofthe left fundus. Apartial posterior hyaloid detachment with traction on the operculum of the hole was observed. A circular punched-out hole was present in the periphery at 2 oclock. Similar lesions are seen in patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and Stickler syndrome, all of which are associated with an increased risk of retinal detachment. Lattice degeneration is a thinning of the retina in the periphery (away from macula). pigmented lattice degeneration was observed. Lattice degeneration occurs in approximately 6–8% of the general population and in approximately 30% of phakic retinal detachments. The cause is unknown, but pathology reveals inadequate blood flow resulting in ischemia and fibrosis. It is an important cause of retinal detachment in young myopic individuals. Degenerations involving the peripheral retina are common in myopes and studies have shown a higher prevalence with increasing grades of myopia.

Lattice degeneration is a disease of the human eye wherein the peripheral retina becomes atrophic in a lattice pattern and may develop tears, breaks, or holes, which may further progress to retinal detachment. Lattice Degeneration - Atrophic Holes - Laser Retinopexy - Laser Indirect Ophthalmoscope. Dilating drops will cause your vision to be blurry for several hours before returning to normal. Detachments due solely to round holes in lattice accounted for almost 2.8 of all retinal detachments treated at Wills Eye Hospital from January 1970 to August 1973. A dilated fundus examination is done by administering dilating eye drops in your eyes to expand the pupil so that the retina can be carefully evaluated. Round atrophic holes in lattice degeneration are an important cause of phakic retinal detachment. The only way to diagnose the condition is with a dilated fundus examination by an eye care provider. It takes on a lattice formation (crisscrossing) because the retinal vessels become sclerotic, and the collagen is laid down in this crisscross pattern. It can be classified as pigmented or non pigmented. Lattice degeneration itself does not cause symptoms LATTICE DEGENERATION: Lattice degeneration is a vitreo-retinal degeneration that causes retinal atrophy (thinning). This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
